Workplace Stress
Statistics
2023
Workplace Stress Statistics
Workplace stress has recently emerged as a significant challenge for employees and organizations worldwide. The latest statistics indicate that stress levels at work are rising, affecting many individuals across different sectors and regions. The detrimental effects of workplace stress on individuals’ physical and mental health, productivity, and overall well-being make it a critical issue to tackle.
Therefore to address this issue, it is crucial to understand the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to mitigate the impact of stress at work.
Key Takeaways
- Employees who experience burnout are 1.8 times more likely to report lower overall job satisfaction.
- 38% of employees report rarely or never discussing their workload with their manager.
- Those with no control over the work schedule have a work-life balance 2.6 times worse than their counterparts.
- Research shows that upper management feels the most stressed compared to other employees (14% vs. 8%).
- Industries with the highest stress levels are healthcare, finance, information, construction and related trades, and food services.
- 23% of women say their job negatively impacts their mental health, while the corresponding figure for men is as low as 16%.
Topics Covered
Impact of Workplace Stress
Causes of Workplace Stress
Global Statistics on Workplace Stress
Demographics of Workplace Stress
Strategies for Managing Workplace Stress
Conclusion
Impact of Workplace Stress
The impact of workplace stress is a topic that has gained significant attention in recent years due to the growing prevalence of stress-related disorders among employees. Work-related stress can have a substantial impact on an individual’s physical and mental health, as well as their productivity and job satisfaction.
Research has found that workplace stress can result in absenteeism, presenteeism, burnout, and increased healthcare costs. Additionally, it can lead to a negative organizational culture, reduced job performance, and high employee turnover rates.
Mental health effects of workplace stress
According to recent data, burnout significantly contributes to employee dissatisfaction and attrition rates. Employees who experience burnout are 1.8 times more likely to report lower overall job satisfaction. Additionally, they are 3.4 times more likely to seek new job opportunities. These statistics underscore the severity of burnout and its impact on employee experience and retention.
Employees who experience burnout are


Causes of Workplace Stress
Various factors, such as job insecurity, long working hours, unrealistic deadlines, interpersonal conflicts, lack of control, and inadequate support from management, can cause workplace stress. These factors can significantly impact an employee’s physical and mental well-being, leading to burnout, anxiety, depression, and other health issues.
Communication breakdown in the workplace causes burnout and stress in employees
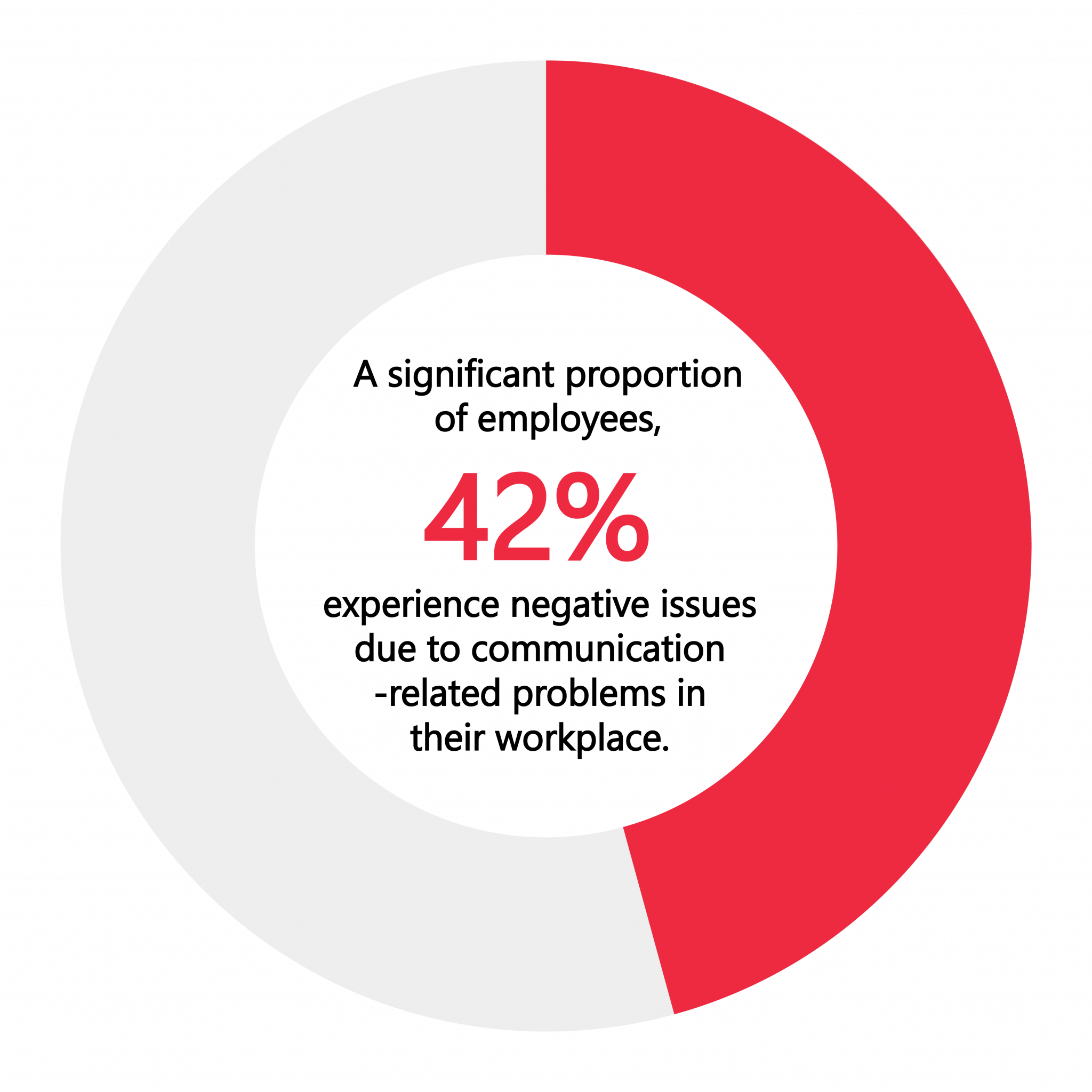
Effective communication is essential to any successful workplace, promoting collaboration, productivity, and job satisfaction among team members. However, when communication breaks down, it can lead to many negative consequences, including burnout, stress, and exhaustion. Research has found that a significant proportion of employees (42%) experience these issues due to communication-related problems in their workplace.
How open are employees to their managers about the stress they experience?
Even acknowledging the issue, 38% of employees report rarely or never discussing their workload with their manager. This reluctance to communicate stems from several reasons, such as the belief that their manager would be indifferent to their concerns (16%) or too preoccupied to address them (13%). Additionally, a significant portion of individuals (20%) hold the view that they should possess the capability to resolve their issues independently.
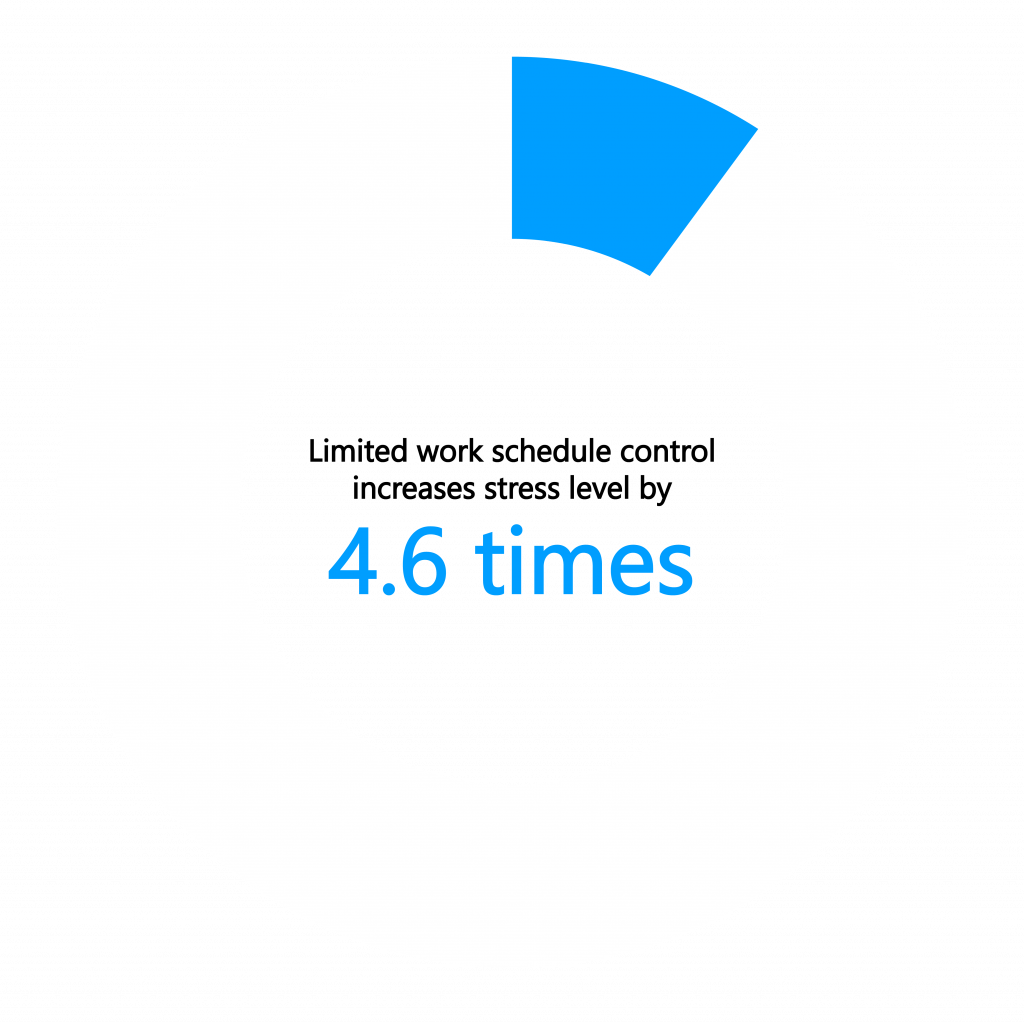
Limited schedule flexibility increases stress levels by 4.6 times for desk workers
According to a recent study, desk workers with limited or no control over their work schedule experience significantly higher work-related stress and anxiety levels, about 4.6 times higher, compared to those with moderate schedule flexibility.
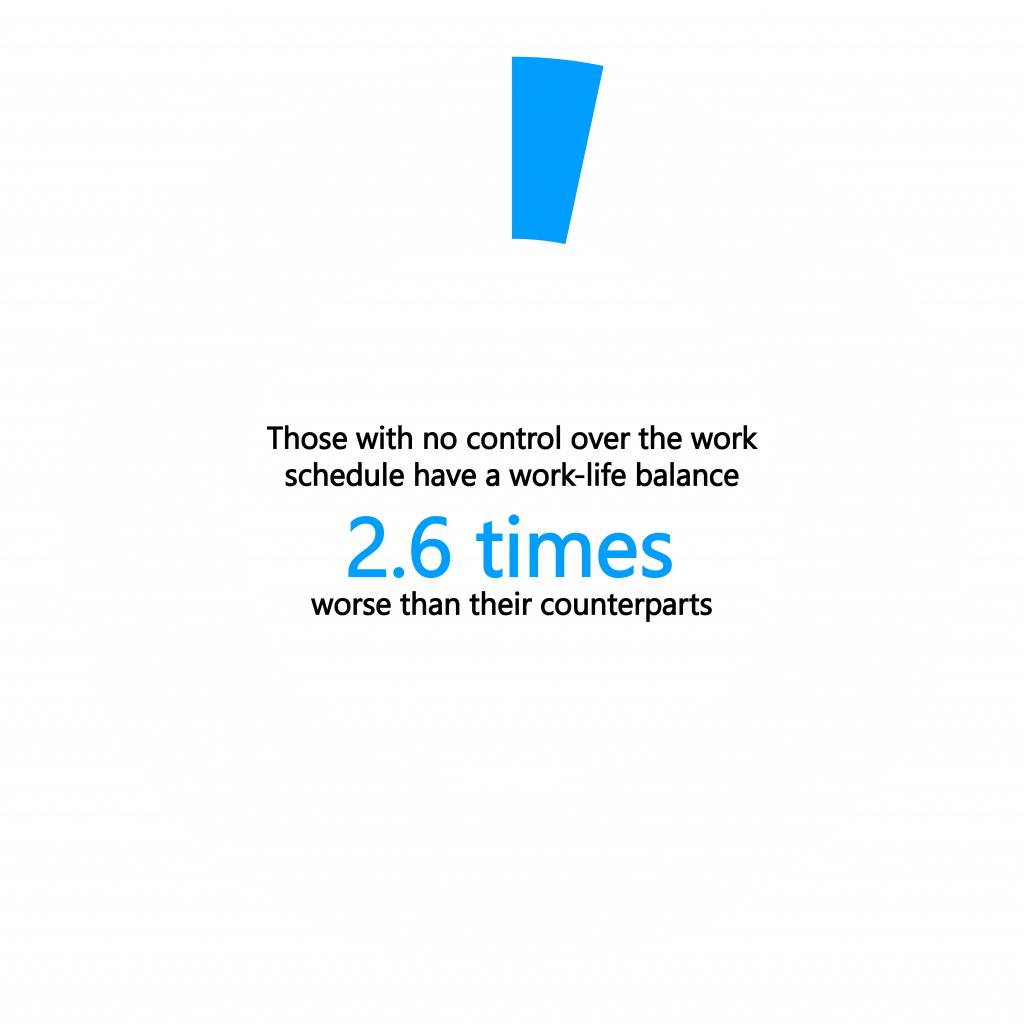
Additionally, the same group of workers reported a worse work-life balance, about 2.6 times worse, than their counterparts who have some control over their work schedule. These findings suggest that having greater control over one’s work schedule may play an essential role in managing work-related stress and achieving a better work-life balance for desk workers.
Slow technology adoption increases employee
burnout risk

Technology highly impacts burnout levels among workers. It is reported that employees who perceive their companies to be slow in adopting technology, also known as laggards, are 31% more likely to experience burnout than those who work for innovative companies. This report indicates that organizations that only incorporate technology after it becomes mainstream have a higher risk of contributing to employee burnout.
Lack of schedule flexibility is linked to increased burnout risk among employees.
According to recent reports, employees who cannot adjust their schedules are more likely to experience burnout at work than those with some schedule flexibility. Specifically, individuals with no control over their work schedules are 26% more likely to report feeling burned out than those with an average ability to shift their schedule
Global Statistics on Workplace Stress
Stress in the workplace is a growing concern around the globe, affecting individuals at all levels of the workforce. While workplace stress is a universal issue, its prevalence and intensity vary significantly depending on the country, work hierarchy, and other factors.
For example, research indicates that workers in Asian countries experience higher levels of workplace stress than in other countries. Additionally, individuals in higher positions of authority tend to experience more stress than those in lower positions.
Workplace stress levels vary by industry
Industries have different stress impact levels on employees due to various factors, including the nature of the work, the status of responsibility and workload, the work environment, and the level of autonomy and control employees have over their work. Industries with the highest stress levels are healthcare, finance, information, construction and related trades, and food services.
Country-to-country variations in employee stress levels
The stress impact levels on employees vary across countries due to various factors, including cultural differences, work-life balance, job security, and social safety nets. For example, some cultures highly value work ethic and may encourage long working hours, while others prioritize leisure time and family life. Specifically, the top 5 states with the highest stress levels are Egypt, India, Japan, Argentina, and Sweden.
Stress by Country
Power dynamics and expectations affect employee stress levels across workplace ranks
Workplace ranks can have different stress impact levels on employees due to power dynamics and expectations placed on individuals at different levels. Those at the bottom of the hierarchy may feel powerless and unsupported, while those in leadership positions may experience pressure to make difficult decisions and manage multiple responsibilities. Research shows that upper management feels the most stressed compared to other employees:
Demographics of Workplace Stress
The manifestation of workplace stress is linked to a confluence of demographic factors, mainly gender and age. Specifically, gender-based societal expectations, pay inequality, and job discrimination are contributory factors that often increase stress among female employees.
In contrast, younger workers may experience elevated stress levels due to concerns surrounding job security and financial stability, while older employees may report stress related to retirement and health issues.
Demographic groups most affected by workplace stress
Recent research has revealed that a significant proportion of the global workforce reports adverse mental health outcomes related to their job. Specifically, one in five employees worldwide, or 20%, experience negative impacts on their mental health due to their job.
However, it’s important to note that gender appears to be a significant factor, with women experiencing a higher prevalence of detrimental mental health outcomes than men. Specifically, 23% of women say their job negatively impacts their mental health, while the corresponding figure for men is as low as 16%.
Gender differences on workplace stress levels
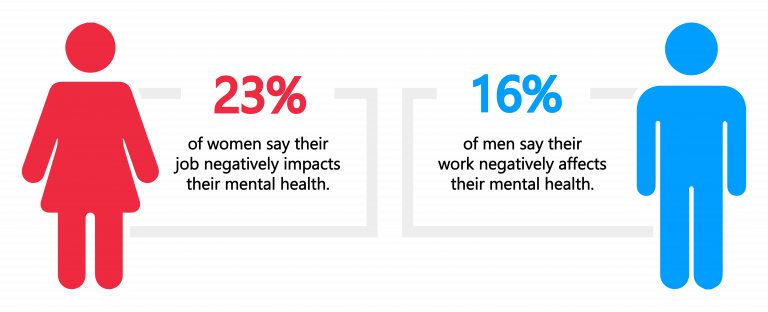
This gender disparity raises essential questions about the underlying mechanisms contributing to this difference. Possible explanations include differences in job demands, job control, social support, and workplace culture. Additionally, societal and cultural factors, such as gender roles and expectations, may exacerbate this disparity.
Strategies for Managing Workplace Stress
Employees must prioritize strategies for managing workplace stress. As stated earlier, unmanaged stress can harm physical and mental health, resulting in burnout, decreased productivity, and increased absenteeism. It can also adversely impact their professional relationships and contribute to a toxic work environment.
By acquiring and implementing stress management techniques, employees can improve their overall well-being, work more effectively, and foster a positive work culture. Ultimately, prioritizing stress management is crucial in maintaining a healthy and fulfilling work-life balance.
Encouraging work-life balance
Employees who struggle with work-life balance are almost 3x more likely to report feeling unmotivated and disengaged at work, identifying themselves as “coasting” or “checked out.” In other words, those who think they cannot balance their professional and personal responsibilities tend to be less invested in their work.

A better work-life balance could benefit these employees by improving their well-being and job satisfaction. Employees with time to pursue their interests and attend to their responsibilities outside of work are likelier to feel fulfilled and happy. They may also experience less stress, better physical health, and stronger relationships with family and friends.
Increasing employee engagement and autonomy
Higher employee engagement and autonomy can positively impact health in the workplace. Employees who feel engaged and invested in their work are more likely to experience a sense of purpose and fulfillment, boosting their mental and emotional well-being.
Additionally, providing employees with greater autonomy and control over their work can reduce feelings of stress and burnout, as they are better able to manage their workload and work at their own pace.
Moreover, autonomy can foster a sense of trust and respect between employees and their managers, leading to better communication, collaboration, and overall job satisfaction. These factors can contribute to a healthier and more productive workplace.
In the United States, there has been a decrease in employee engagement for the first time in ten years. The percentage of engaged employees went down from 36% engaged employees in 2020 to 34% in 2021. This trend continued into 2022, with just 32% of full-time and part-time workers feeling engaged in their work while 17% are actively disengaged, representing a 1% point increase from the previous year.
U.S. Employee Engagement Trend, Annual Averages
Providing adequate resources and support
Providing adequate resources and support for mental health is a moral imperative and a crucial step toward fostering a productive and healthy workforce. According to a recent survey, the majority of employees across the globe, precisely 81%, indicated that they would prioritize their mental health over receiving a high salary. Furthermore, 64% of respondents acknowledged that they would be willing to accept a reduced salary for a position offering better mental well-being support.
8 out of 10 employees would prioritize their mental health over a high salary

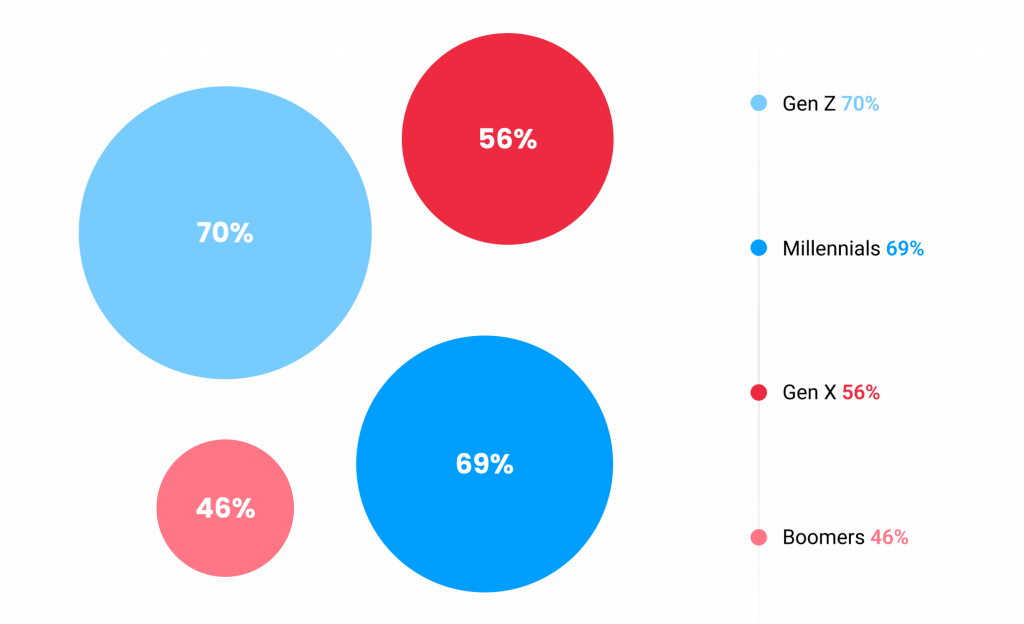
However, it is worth noting that there is an important distinction between generations regarding this issue. Younger employees are more likely to prioritize mental health over a high-paying job compared to older employees (70% vs. 46%):
Mental health prioritization by generation
Conclusion
The statistics on workplace stress are alarming and cannot be ignored. Many employees report stress-related health issues and reduced productivity, so organizations must proactively address workplace stress.
Employers should implement stress management programs, provide work-life balance options, and encourage employees to take breaks and prioritize their mental and physical health. Employers can improve employee well-being, reduce turnover rates, and drive business success by creating a supportive, stress-free work environment.